What Is the Ground in Electricity: Meaning and Function
Grounding is an essential concept in electricity, as it ensures safety, equipmen...

A crucial step in the digital transformation of enterprises is the implementation of data center virtualization. It enables businesses to completely forget about using ordinary servers by giving preference to a highly flexible and easily scalable IT setups. Modern enterprises increasingly implement and rely on virtualization so that to streamline their IT resources, minimize their expenditure, and improve fault tolerance.
Suppose you’re actively trying to figure out what data center virtualization is. In that case, you should realize that it serves as a powerful tool for the consolidation of various hardware components, flexibility enhancement, and cost minimization. As opposed to on-premise setups, this innovative approach also enables you to gain access to data and applications from afar.
Data center virtualization is closely tied to cloud technologies. It involves moving physical servers, storage, and network components into a software-defined environment. This allows for quick resource reassignment and scaling based on the evolving needs of a business. This makes it possible to promptly reassign and reallocate resources with due regard to the current needs and requirements of a particular business.
The cloud model involves the usage of a virtual data center, i.e., a software-driven IT setup. It can be deployed on a vast variety of public, private, or hybrid cloud-based platforms. Companies can reap a tangible benefit from phenomenal flexibility and the ability to adapt the chosen solution to the ever-changing market conditions.
Almost everyone knows that both cloud computing and hybrid infrastructures become more and more popular day by day. For this very reason, finding an answer to the question “What is data center virtualization?” is of paramount importance to organizations striving to maintain their competitive ability in the digital universe.
The heart of the virtualization process is a hypervisor (virtual machine monitor). This software can create, control, and manipulate virtual machines. Each VM serves as a standalone server with its own computational resources, such as a central processing unit, RAM memory, storage space, network bandwidth, and an OS.
The vast majority of modern IT setups rely on data centers and virtualization architecture to boost performance, minimize needless expenses, and improve scalability. This renders it probable to run several instances of an OS on the same computer with the use of the same equipment and guarantee their streamlined functioning.
A hypervisor will enable you to use physical resources on multiple VMs without causing any kind of conflicts between them. It means that different OS and apps can operate simultaneously on the same physical server.
One can easily transfer VMs between servers without interrupting their operation, which guarantees a very impressive fault tolerance level. Thanks to this approach, IT administrators and other technical experts can control the entire infrastructure centrally. On top of that, they can automate a wide array of processes and adjust virtual resources in such a way as to make them solve the tasks at hand.
Data center virtualization is one of the major steps on the path to creating an adaptable, economically viable, and scalable IT setup. It enables companies to boost operational reliability, decrease expenses, and appropriately manage resources in the continuously evolving digital universe.
It’s not so hard to guess that virtualization will become in the future an integral part of the development of cloud-based technology, automated IT processes, and artificial intelligence in the business world.

Grounding is an essential concept in electricity, as it ensures safety, equipmen...
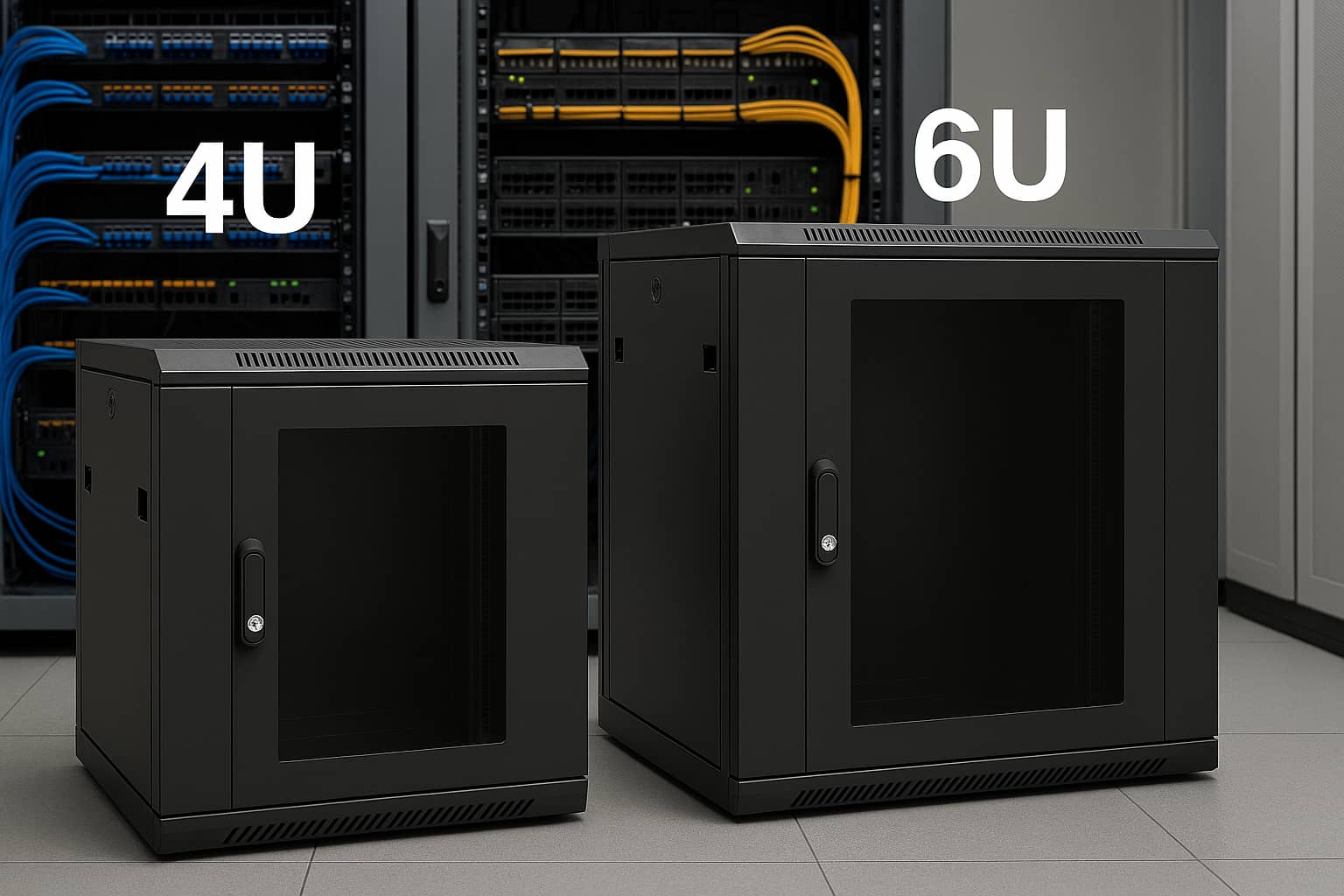

A rack unit (U) is one of the key dimensions in the telecom industry. The parame...

Servers come as indispensable elements of a network infrastructure. They serve a...