What Is the Ground in Electricity: Meaning and Function
Grounding is an essential concept in electricity, as it ensures safety, equipmen...

Network hardware requires constant feeding to ensure smooth operation. IT equipment consumes a lot of power when performing calculations and processing data. At the same time, it emits too much heat, which can lead to multiple problems.
Energy supply and data center cooling are interconnected since the data center rack’s power consumption level depends on the data center’s climatic conditions. Moreover, ventilation tools consume electricity as well, meaning that the extra capacity of a PDU should be left to feed all components of an IT system. Thus, it is necessary to regard all the objects stored in server rooms as a single complex unit when calculating server rack power requirements.
The server rack energy consumption issue is topical since it has many units requiring sufficient feeding. A server cabinet is a storage place for highly computing equipment, where each device requires powering. When the number of devices totals several hundred or even thousands, consumed energy rises exponentially.
Another important issue is powering other servicing units, such as cooling devices. When in operation, IT hardware tends to heat well. The need for forced ventilation tools (fans, evaporators, etc.) arises when we accumulate the heat produced by all equipment components.
Consequently, one server rack has multiple units that require feeding. Data centers can have dozens of racks, meaning that the need for power increases drastically. Thus, tech staff and maintenance employees should take time and effort to calculate the amount of the required power to feed one rack and an entire center, taking into account average server rack power consumption, which typically ranges between 3 and 5 kW per rack but can reach 10–15 kW for high-performance setups.
The primary purpose of calculating the needed energy consumption is related to the fact that power distribution units can produce different amounts of energy. Each station has a maximum capacity of produced power, meaning that if your system requires more energy, some units will lack feeding. Sufficient feeding of all units is vital for communications systems; otherwise, they will work improperly, resulting in malfunction, downtime, and breaking. This is why it is essential to ensure that the available power distribution unit can generate the required energy to feed all devices, considering data center power consumption per rack.
When settling a server infrastructure, remember that stronger and more powerful servers compute more complicated tasks and deal with large amounts of information, emitting more heat. Thus, they require more cooling devices. Make sure to surrender powerful servers with a sufficient number of coolers. At the same time, the need to feed fans and coolers will also increase the power capacity of the PDU.
A PDU is an obligatory element of the network system’s energy supply. Considering ampere requirements, technicians can configure and adjust the power supply to all units to feed all modules and racks with sufficient power. Besides, PDUs perform other functions, such as environmental monitoring and remote access. One of the main tasks of system administrators is to calculate the needed capacity of the PDU to guarantee proper feeding. Also, PDUs provide remote access and environmental monitoring options to simplify handling and guarantee security.
A too-weak PDU will result in the following problems:
Sufficient power consumption of the server room guarantees a smooth and continuous performance of system units.
When planning server feeding, connecting devices to appropriate power supplies is vital to guarantee stable and uninterruptible functioning. Even a short-time server breakout can cause data and money loss, which results in significant expenses to businesses and infrastructures. Thus, when connecting servers, take into account their power needs.
Energy is critical to powering data centers and maintaining optimal operating conditions.
Here, also note that an IT system accommodated in a data center is a complex organism where each unit and component needs electricity. Depending on a device, its power, and its capacity, the level of consumed energy differs. Some objects are less power-consuming, while others set higher requirements for energy supply. For instance, large servers require more powerful feeding and cooling. Thus, you should understand how power is allocated within the data center. Here are some figures that will help calculate and allocate energy correctly:
Yet, note that although the share of digital processes rises annually, an average server room power consumption has increased by 6% between 2000 and 2018, demonstrating that it is possible to figure out a power-effective strategy for running DCs.
Surprisingly, a significant portion of every supply goes into maintaining a proper environment in DCs, so it is essential to consider cooling issues attentively and pick low-energy, high-efficiency devices for cooling purposes.

As you see, the issue of DC feeding is complicated since too many aspects require consideration. Now, let’s see how to determine power consumption in the server room. This detailed guide will explain how to allocate energy efficiently and avoid mistakes in calculations:
Technicians can use another method to determine the required server room power consumption. They can observe it in real-time or determine how much energy is supplied to the data center and divide the figure by the number of units. Yet, this approach is more general and does not allow for a precise estimate for each cabinet or rack.
Also, when dealing with the power issue, note that two different types of loads are distinguished: server room steady state vs peak power consumption. The steady-state indicator is usually considered an average figure that the PDU must satisfy. Yet, when selecting a suitable PDU model, ensure it is robust enough to withstand peak energy consumption.

Grounding is an essential concept in electricity, as it ensures safety, equipmen...
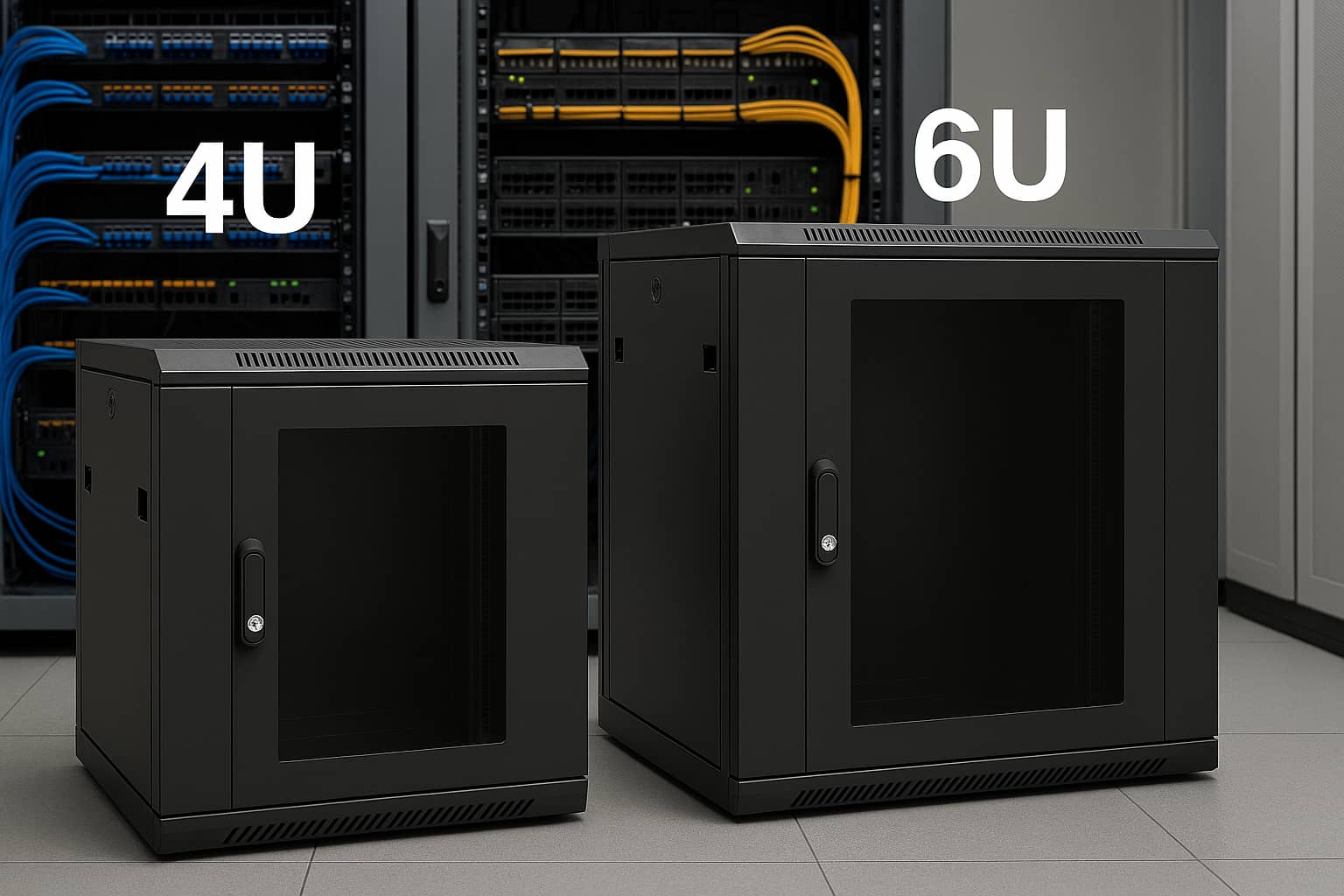

A rack unit (U) is one of the key dimensions in the telecom industry. The parame...

Servers come as indispensable elements of a network infrastructure. They serve a...