What Is the Ground in Electricity: Meaning and Function
Grounding is an essential concept in electricity, as it ensures safety, equipmen...

Any network system requires feeding. Server setups consist of hardware that consumes energy during operation. Thus, the issue of energy management is essential in this field. In this regard, an UPS (Uninterruptible Power Supply) and a PDU (Power Distribution Unit) come as two essential devices that enable uninterruptible and sufficient feeding of all system components.
However, although they are often used together in server racks, they serve very different functions. In this article, we’re going to answer the question «what is the difference between a PDU and a UPS?» and discuss the features of both devices.
The UPS is one of the obligatory devices of network systems. It is used to provide temporary backup energy supply and protection to electronic equipment during power outages or fluctuations. The device serves as a safeguard, ensuring that sensitive network hardware can continue to operate uninterruptedly even in the event of an electricity failure. The presence of such devices in a network chain allows for preventing sudden shutdowns and potential data loss.
When a power outage occurs, the UPS instantly switches to battery power, allowing connected devices to keep running for a limited time. This consequence is essential for preserving data integrity in networking equipment that requires a stable power supply to prevent disruptions.
There are different types of UPSs, including standby, line-interactive, and online ones. The issue of choosing the right type of UPS is essential since it can make a difference in ensuring device uptime and protecting valuable data from unexpected power issues.
The PDU is a device installed in network systems to distribute electrical power from a single input source, such as an Uninterruptible Power Supply (UPS) or a wall outlet, to multiple rack-mounted components, such as servers and other electronic devices. They are widely used in data centers and server rooms. PDUs play a vital role in managing power delivery within racks. The device ensures efficient operation, improves uptime, and facilitates streamlined organization of power resources.
When considering the essence of PDUs, it’s important to understand that they do not have batteries and do not provide backup power. Their primary role is to distribute power between all system components. Thus, such devices serve as a power source. They enhance energy allocation within a rack, which is essential for maintaining a well-functioning and efficient server environment. Advanced models are equipped with monitoring and switching capabilities, which allows for improving operational efficiency and enabling remote control. These features greatly contribute to minimizing downtime and preventing power-related issues.

Now, you’re aware of the specifics of both devices. So, let’s precede the comparison of PDU vs UPS. Below, you’ll find why and in what way both power devices differ.
The core difference between the UPS and the PDU lies in their primary functions within an energy system. The UPS is designed to protect equipment from energy failures and inconsistencies, such as voltage spikes, sags, and complete outages. It copes with this task by providing backup battery electricity and filtering electrical noise. The device is usually the first link in the energy supply chain, which allows for guaranteeing that devices receive consistent and stable power.
In contrast, the PDU focuses on managing how energy is distributed to various devices and equipment. It is typically placed downstream of the UPS in the power setup. While the UPS actively responds to electrical issues by switching to battery power when necessary, the PDU is a more passive or semi-active device. The latter is responsible for organizing and controlling the distribution of power to multiple outlets, ensuring that all connected equipment receives the required power without overloading circuits.
Here is a comparative table of both devices, with the key features listed:
| Feature | UPS | PDU |
| Primary function | Protects against voltage fluctuations | Distributes electricity to multiple devices |
| Position in power chain | First link in the energy supply chain | Follows the UPS in the setup |
| Power backup | Provides battery backup during outages | No backup capability |
| Response to issues | Actively responds to electricity-related issues | Passive/semi-active control |
| Voltage regulation | Often includes voltage regulation and filtering | Generally does not perform these functions |
| Equipment protection | Protects connected devices from surges and interruptions | Primarily for energy distribution, not protection |
| Control features | May offer monitoring and management features | Often includes monitoring, circuit breakers, and control features |
| Typical use cases | Critical systems needing immediate power backup | Data centers, server rooms, and applications requiring organized distribution |
In summary, the UPS is an essential tool for anyone relying on sensitive equipment. Whether in home offices, network closets, or data centers, choosing the right type of UPS can make a significant difference in ensuring device uptime and protecting valuable data from unexpected power issues. PDUs are invaluable components in modern data centers, aiding in the efficient and organized distribution of electrical power to ensure that critical systems operate reliably and effectively. Both devices are crucial for DC infrastructures. However, note that they are not interchangeable. Both devices perform their unique functions and are responsible for different aspects of network infrastructures.

Grounding is an essential concept in electricity, as it ensures safety, equipmen...
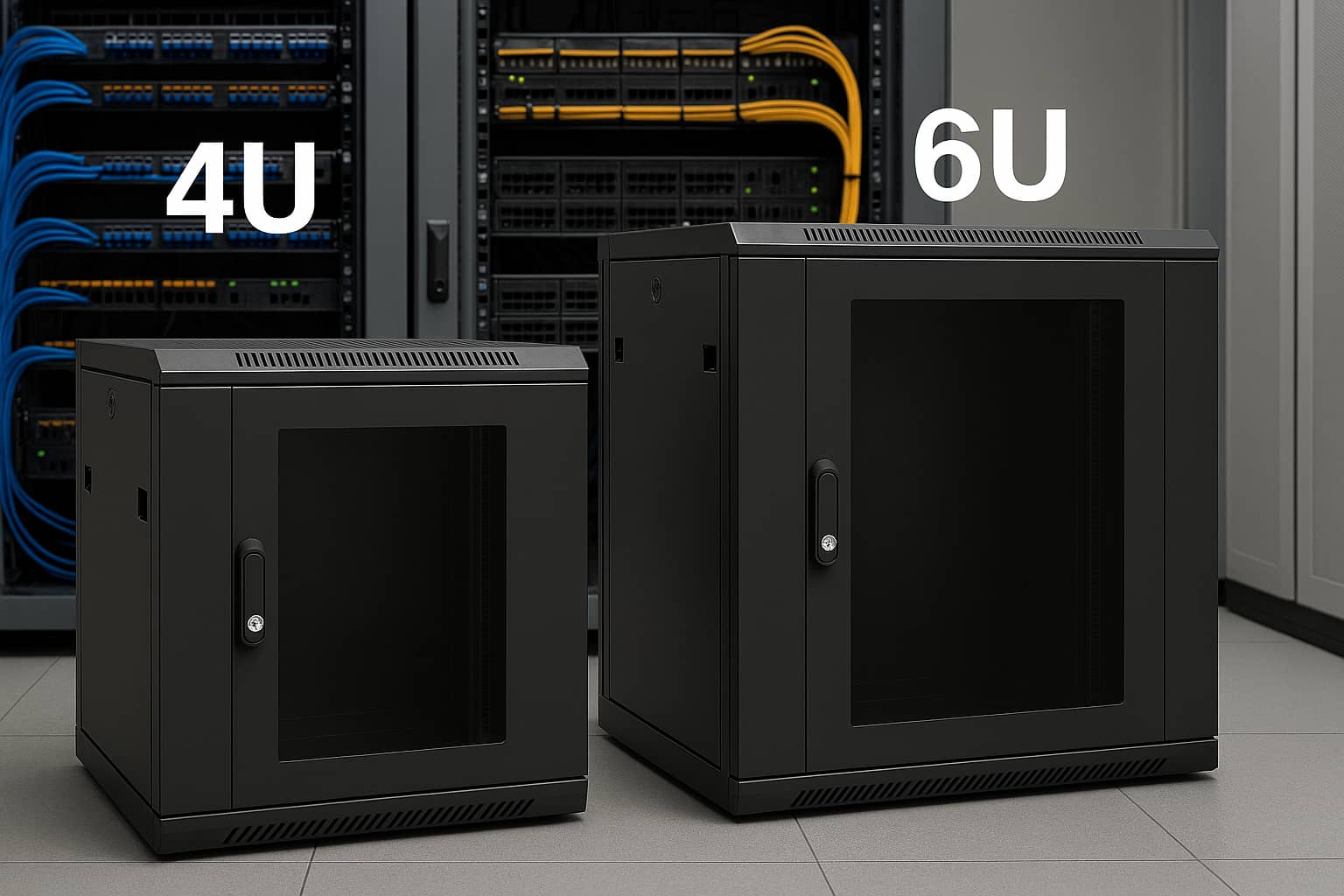

A rack unit (U) is one of the key dimensions in the telecom industry. The parame...

Servers come as indispensable elements of a network infrastructure. They serve a...